Basic Information
Dynamic load management (DLM) adapts the charging currents to the available electricity and is designed as local load management. Charging points are connected via a network connection and can be configured via the user interface.
Technical Requirements
The house connection, supply line or sub-distribution can determine the upper limit of the charging current. Dynamic load management enables the distribution of reserves of unused charging points to other charging points.
Operating modes
Load management without external measurement: Fixed upper limit of the electricity to be distributed.
Load management with external measurement: Dynamic adjustment of electricity based on total consumption.
Phase-individual load management
Takes into account whether a vehicle is charging single-phase or three-phase in order to distribute the load optimally.
Avoids asymmetric loads
Prevents uneven loading of the phases to meet grid requirements.
Load management operating modes
The load management system has various operating modes and options for optimizing the load on the basis of availability and consumption. Depending on how a system is structured, alongside the charging points there are sometimes loads that cannot be controlled (e.g., loads in a property or building/commercial establishment) and of course have an influence on the total amount of available current.
For this reason, the most common configurations are:
Load management without additional loads (and therefore without external measurement)
Load management with additional, partially unknown loads and external measurement
Both cases are there to distribute charging current optimally and to avoid overstepping a definable load limit in order to prevent overload.
Observe the minimum charge current
Certain vehicles only start charging when a certain amount of energy is available. The value is 1.38 kW for single-phase systems and 4.14 kW for three-phase systems. The minimum available charging power must be available for the vehicle to start charging. If not, the vehicle may “fall asleep”, i.e. even if more charging power is then available again, the vehicle will not start charging. In most cases, the charging process must then be stopped and restarted on the vehicle.
Connection example of load management without external power measurement

Connection example of 3 charging stations without external power measurement
Connection example of load management with external power measurement
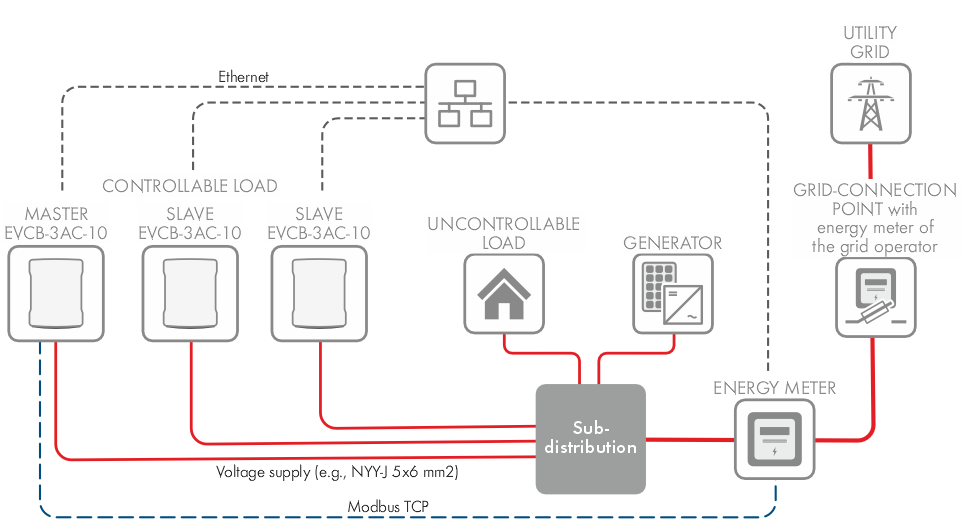
Connection example of 3 charging stations with external power measurement
